The Controller#
Controllers are the main interfaces through which operators can set up and alter the state of a Constellation. Currently, the framework provides two different controllers, a graphical user interface and a scriptable interactive command-line interface.
Schematic drawing of CSCP#
See also
A detailed technical description, including protocol sequence diagrams, can be found in the protocol description chapter in the framework development guide.
Graphical Controller#
The MissionControl graphical user interface is a general purpose controller for Constellation based on Qt which allows loading and parsing of configuration files, deduction of the configuration from a running Constellation, and common control of all active satellites as well as each individual satellite. This section briefly describes these features and the user interface.
See also
The tutorials section provides a step-by-step guide on Using MissionControl.
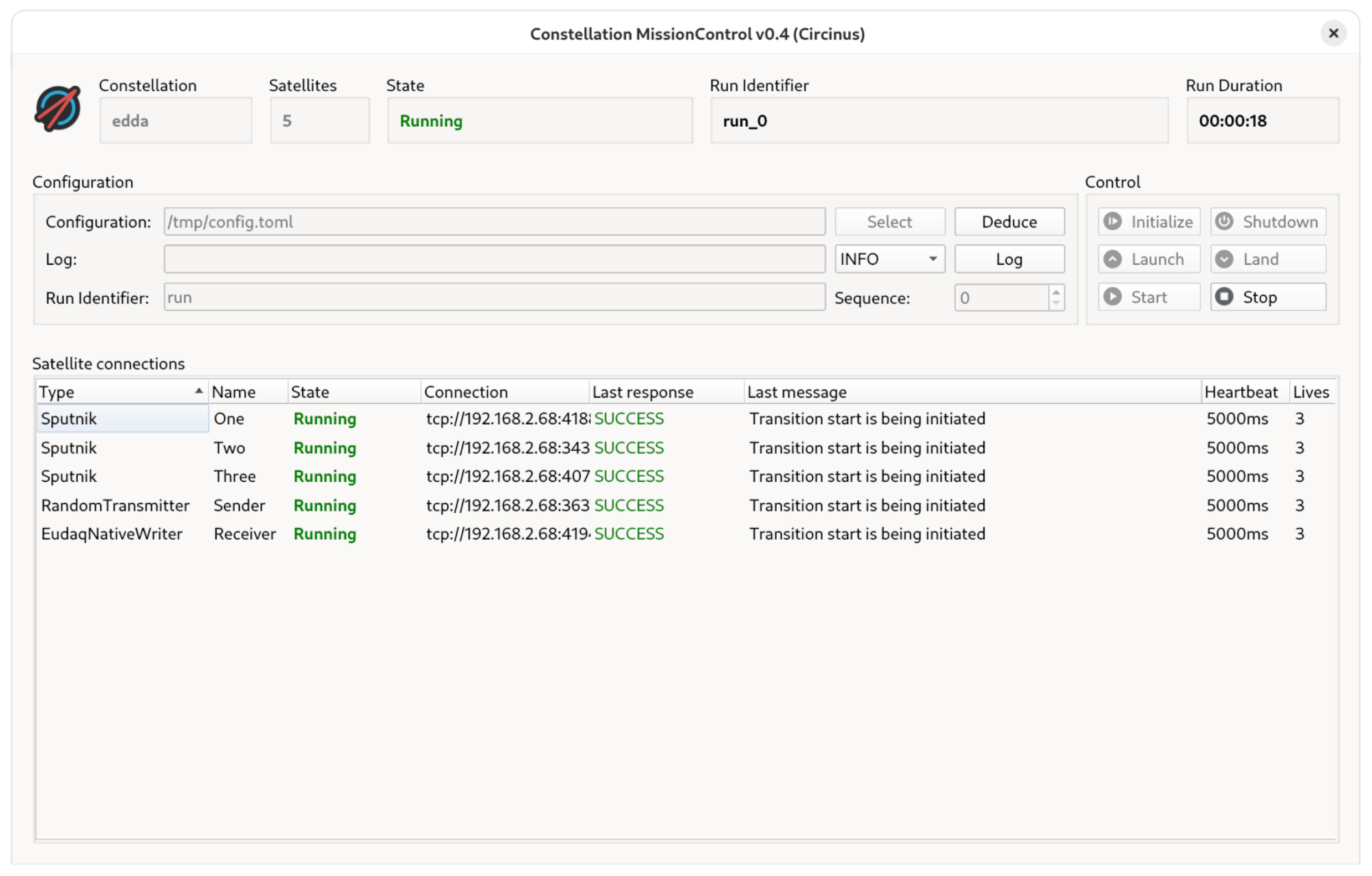
Main window of the MissionControl controller#
The main window of MissionControl is divided into three parts: The header portion displays information on the Constellation which the controller is connected to, such as its name, the number of satellites and the global state. Here, the global state is a summarized state of all satellites. It represents the lowest state of any individual satellite, and, if not all satellites are in the same state, is amended by the symbol ≊ to indicate a mixed global state, e.g. INIT ≊ for a constellation where all satellites are initialized but one is already launched. Furthermore, the current or last run identifier along with its run duration are displayed. None of this information is stored locally; instead, it is all fetched from the running Constellation upon startup of the controller.
The section below the header is the control area steering the entire Constellation at once. The input fields allow selection of the configuration file, dispatch of log messages by the operator, and setup of the run identifier. The buttons on the right serve as control for the satellite finite state machine. Buttons for transition commands unavailable in the current global state are deactivated and grayed out.
Finally, the lower part of the main window is occupied by the list of all connected satellites of the Constellation.
The type and name of each satellite are displayed alongside its current state, the last command response and the current CHP heartbeat interval and remaining lives. Double-clicking a satellite item from the list opens a dialog with additional connection details.
A context menu provides direct access to the commands of the individual satellite, including transitions and possibly defined custom commands.
All information is obtained directly from the running satellite and does not depend on any local cache or pre-loaded information in the controller.
In case a command returns payload information, such as the get_config command, a dialog window displays this to the operator.
While the run identifier is a free-form string, this controller defines it as a name followed by a sequence number. The sequence number is automatically incremented when stopping and starting a run, such that a unique run identifier is always generated and sent to the Constellation.
Since satellites operate independently of the controller, and controllers can be started and closed at any time, they might not necessarily all have access to the same configuration file. To alleviate this, the configuration of all satellites can be deduced from the Constellation in operation directly via the Deduce button of the controller. This will collect the current configuration from all connected satellites and open a dialog window to select a storage location for the configuration file.
Scriptable Controller#
In some scenarios, a scriptable command-line interface might be preferable to a graphical user interface. For this purpose, a Python controller class is provided, both as standalone script and as interactive shell based on IPython. Individual satellites as well as the entire Constellation can be queried and controlled directly through the ScriptableController class. Complex routines such as automated parameter scans can be implemented in a few lines of Python code.
import time
from constellation.core.controller import ScriptableController
# Create controller
ctrl = ScriptableController(group_name)
constellation = ctrl.constellation
# Initialize, launch and start:
cfg = load_config("my_config.toml")
constellation.initialize(cfg)
ctrl.await_state(SatelliteState.INIT)
constellation.launch()
ctrl.await_state(SatelliteState.ORBIT)
constellation.start("run_1000")
ctrl.await_state(SatelliteState.RUN)
# Run for 15 seconds
time.sleep(15)
constellation.stop()
ctrl.await_state(SatelliteState.ORBIT)
See also
The How-To section provides a guide on Parameter Scans with Python.
Measurement Queues#
Measurement queues are a sequence of runs which are processed one after the other, either with the same or altered parameters for the constituents of the Constellation. Some controllers support measurement queues to automatically reconfigure the Constellation, e.g. to scan through parameter ranges. Individual measurements consist of
A list of satellites and a configuration object for each of them, with the parameters to be changed
A condition which determines the end of the measurement. This could for example be a duration or a specific value of a metric one of the satellites emits.
Measurement Procedure#
Usually, measurement queues will require a fully initialized and launched Constellation to operate on.
When started, the measurement queue will pick up the first measurement, send the reconfigure command to all satellites
which have configurations in the measurement, wait for the reconfiguration to succeed and then start a run. The run
identifier is usually generated from a configured prefix and a sequence number referring to the current measurement in the
queue.
The Constellation is then kept in the RUN state until the condition of the measurement expires, e.g. the duration timer reaches its timeout, or the configured metric has reached its target value or threshold.
The queue then emits the stop command and waits until all satellites have reached the ORBIT state again before continuing
with the next measurement in the queue.
Original Configuration Values#
A queue may contain scans of different parameters. In order to avoid configuration parameters from the previous measurement
to remain active, the original values of each measurement parameter are read from the satellites using the get_config command before the measurement is started and are cached in the queue. Whenever a parameter does not appear in the new
measurement anymore, it is reset to the original value the next time a reconfiguration is performed.
For example, a queue that contains three measurements for the same satellite, first setting the parameter a to values 1
and 2, and the parameter b to value 5 will first read the parameter a from the satellite configuration (e.g. a = 99), then set
a = 1 for the first measurement and a = 2 in the subsequent measurement.
The final measurement will set b = 5 as well as parameter a = 99 to its original value initially read from the satellite.
When implementing queues manually e.g. through a Python script as described in the How-To Guide, the original value has to be cached and reconfigured by the script.
